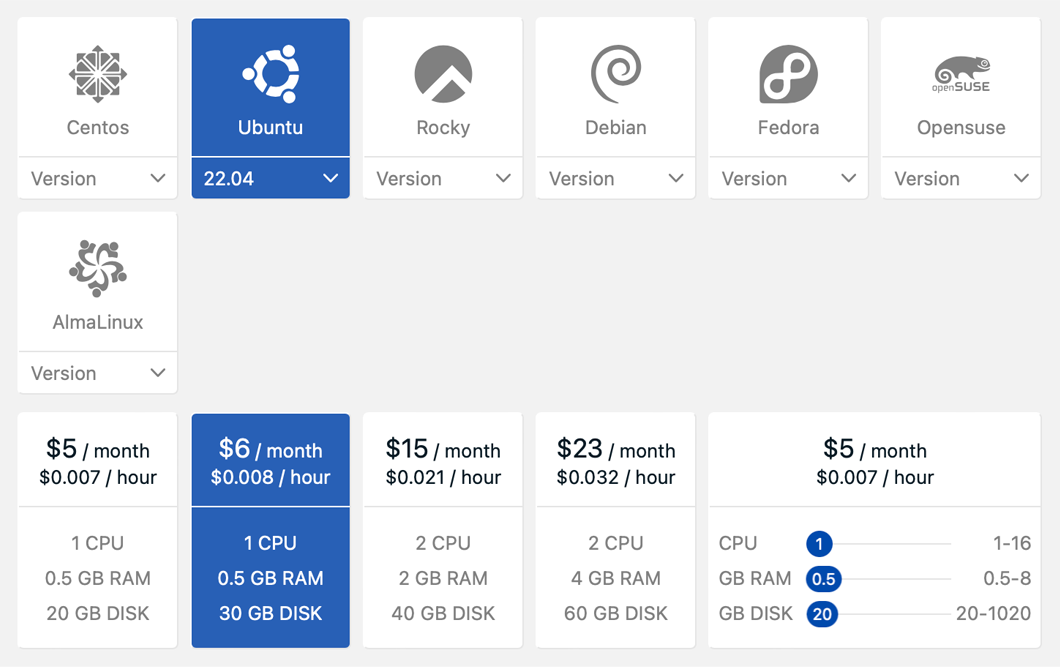
Virtual Machines (VM)
Access your Virtual Machines through a public network, within the platform, or via a console panel. External public IP addresses are provisioned as floating IPs, meaning you can keep the IP or assign it to another machine, even if the original VM is deleted.
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
A mark of any real cloud platform is the ability to create Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) networks. Build VMs and assign them quickly to different VPCs with ease–at no additional cost.
Virtual Machine Features
Virtual Machines offer the capability of a physical computer system, including a processor, memory, disk storage, and network connectivity, all encapsulated in a software emulation. Here are some key features:
- Isolation: Each VM is isolated from its host physical system and other VMs, providing a secure and independent operating environment.
- Resource Management: VMs have their own set of resources (RAM, CPU, storage) allocated by the host system, allowing for efficient distribution and usage.
- Versatility: VMs can run any operating system compatible with the underlying hardware, making them highly versatile for different applications.
- Snapshots and Cloning: VMs can take snapshots of the current state, which can be used to return to the same state later. VMs can also be cloned to create an identical copy.
- Live Migration: This feature allows VMs to move from one host to another while keeping applications online, ensuring high availability and load balancing.
Virtual Private Cloud Features
A Virtual Private Cloud is a secure, isolated private network in the cloud where resources are not shared with others. It provides a secure environment for running applications. Here are the key features:
- Security: VPCs offer high levels of security by providing a private section of the cloud with controlled access, allowing you to use your IP address ranges, subnets, network gateways, and security settings.
- Scalability: You can quickly scale resources up or down based on demand, paying only for what you use.
- Network Control: VPCs allow advanced networking features such as subnet creation, route table definitions, network gateways, and security settings.
- IPV6 Support: VPCs often support IPv6, the most recent version of the Internet Protocol, ensuring your services are future-proofed.
- VPN Connection: You can connect your on-premise data center to a VPC via a secure VPN connection, making it an extension of your data center.
- PrivateLink: VPCs usually offer a service like AWS PrivateLink that securely accesses services hosted on the VPC without exposing traffic to the public internet.
These features enable businesses to efficiently utilize cloud computing resources, providing scalability, flexibility, and security. Virtualization is a powerful tool, allowing companies to reduce costs, improve system recovery, and manage workloads efficiently.